Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 serves as the cornerstone of electrical equipment protection, providing a comprehensive roadmap for safeguarding electrical systems against potential hazards. Delve into this detailed analysis to uncover the intricacies of this essential table, ensuring optimal safety and compliance in your electrical installations.
Within the framework of Table 8.3.1, you’ll discover a systematic approach to protecting various types of electrical equipment, encompassing specific requirements tailored to each category. Explore the diverse protection methods Artikeld in the table, gaining insights into their mechanisms, advantages, and limitations.
Table 8.3.1 Overview
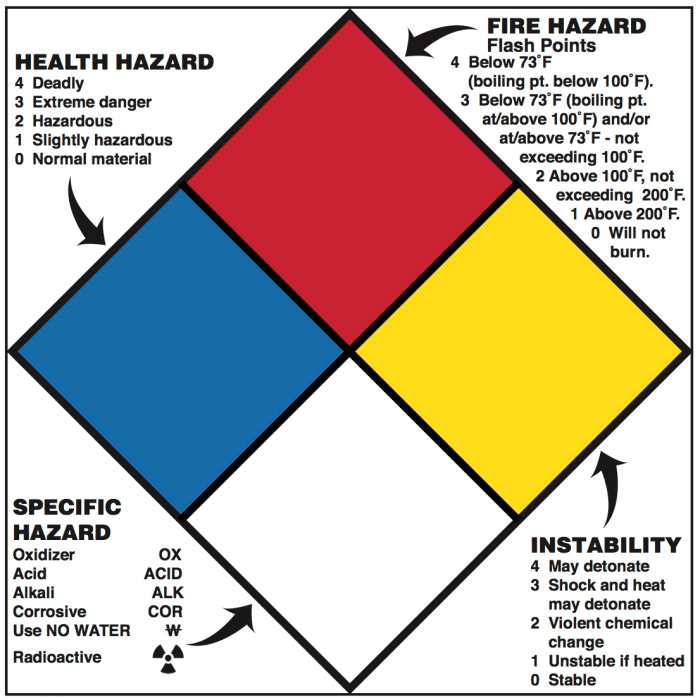
Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10, titled “Conductors – Properties of Insulated Conductors,” plays a crucial role in the electrical industry by providing essential information on the properties of insulated conductors used in electrical systems.
Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 provides crucial data for electrical installations. If you’re curious about “ohms per 1000 feet NEC,” check out this informative resource . It covers the topic thoroughly, and upon returning, you’ll find more valuable insights in Table 8.3.1 of NFPA 10.
The table is organized into several columns, each presenting specific characteristics of insulated conductors, such as conductor material, insulation material, maximum operating temperature, voltage rating, and minimum bending radius. This comprehensive data enables electrical professionals to make informed decisions when selecting and installing insulated conductors in various electrical applications.
Conductor Materials
Table 8.3.1 lists various conductor materials commonly used in electrical systems, including copper, aluminum, and copper-clad aluminum. Each material possesses unique properties that influence its suitability for different applications. For instance, copper is known for its high electrical conductivity and is often used in power transmission and distribution systems.
Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and cost-effective, making it suitable for overhead lines and service entrance conductors.
Insulation Materials
The table also provides information on insulation materials used to protect conductors from electrical hazards and environmental factors. Common insulation materials include rubber, thermoplastic, and thermosetting polymers. Each material offers different levels of electrical resistance, mechanical strength, and temperature tolerance.
Understanding the properties of insulation materials is crucial for selecting the appropriate insulation for specific electrical applications.
Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 provides essential guidelines for electrical installations. Speaking of literature, have you tried the Raisin in the Sun quiz ? It’s a great way to test your knowledge of the play. Anyway, back to Table 8.3.1, it covers topics such as wiring methods, overcurrent protection, and grounding.
By adhering to these standards, you can ensure the safety and reliability of your electrical system.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The maximum operating temperature of an insulated conductor is a critical factor to consider when designing electrical systems. Table 8.3.1 specifies the maximum temperature at which each conductor can operate safely without compromising its integrity or insulation properties. Exceeding the maximum operating temperature can lead to insulation breakdown, conductor damage, and potential electrical hazards.
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of an insulated conductor indicates the maximum voltage it can withstand without electrical breakdown. Table 8.3.1 provides voltage ratings for different types of insulated conductors, allowing electrical professionals to select conductors that meet the voltage requirements of their electrical systems.
Using conductors with an insufficient voltage rating can result in insulation failure and electrical hazards.
Minimum Bending Radius
The minimum bending radius of an insulated conductor is the smallest radius to which it can be bent without damaging the conductor or insulation. Table 8.3.1 specifies the minimum bending radius for each type of insulated conductor, ensuring that conductors are installed correctly and maintain their integrity during bending operations.
Ignoring the minimum bending radius can lead to conductor damage, insulation cracking, and potential electrical hazards.
Types of Electrical Equipment

Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 covers a wide range of electrical equipment, each with specific requirements. Understanding these types and their requirements is crucial for ensuring electrical safety and compliance.
Electrical Conductors
- Conductors are materials that allow electricity to flow through them.
- Table 8.3.1 specifies requirements for the ampacity, insulation, and installation of conductors.
- Properly sized and insulated conductors prevent overheating and electrical hazards.
Overcurrent Protective Devices
- Overcurrent protective devices (OCPDs) are designed to interrupt the flow of excessive current.
- Table 8.3.1 provides guidelines for selecting and installing OCPDs, such as circuit breakers and fuses.
- OCPDs protect electrical circuits and equipment from damage caused by overcurrents.
Enclosed Switches and Circuit Breakers
- Enclosed switches and circuit breakers are used to control and protect electrical circuits.
- Table 8.3.1 specifies requirements for the construction, installation, and maintenance of these devices.
- Properly installed and maintained switches and circuit breakers ensure safe operation and prevent electrical accidents.
Motor Controllers
- Motor controllers are devices that regulate the operation of electric motors.
- Table 8.3.1 provides guidelines for selecting and installing motor controllers.
- Properly selected and installed motor controllers ensure efficient and safe operation of motors.
Transformers, Table 8.3.1 in nfpa 10
- Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another.
- Table 8.3.1 specifies requirements for the installation and maintenance of transformers.
- Properly installed and maintained transformers prevent electrical hazards and ensure reliable power distribution.
Protection Methods
Table 8.3.1 Artikels several protection methods for electrical equipment, each with its advantages and disadvantages. These methods aim to prevent or mitigate electrical hazards, ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Protection methods fall into two broad categories: active and passive. Active methods involve actively detecting and responding to electrical faults, while passive methods rely on physical barriers or inherent design features to prevent faults or limit their consequences.
Active Protection Methods
- Overcurrent Protection:Detects and interrupts excessive current flow using devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and relays. Advantages: Fast response, high reliability, cost-effective. Disadvantages: Can be susceptible to nuisance tripping.
- Ground Fault Protection:Detects and interrupts current flow to ground using ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) or residual current devices (RCDs). Advantages: Protects against electrical shock hazards. Disadvantages: Can be sensitive to ground loops and moisture.
- Arc Fault Protection:Detects and interrupts electrical arcs using arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs). Advantages: Prevents electrical fires caused by arcing faults. Disadvantages: Can be sensitive to normal electrical noise.
Passive Protection Methods
- Insulation:Non-conductive material that prevents current flow between conductors. Advantages: Prevents electrical shock, reduces heat loss. Disadvantages: Can degrade over time, requires maintenance.
- Enclosures:Physical barriers that prevent access to live parts. Advantages: Protects against accidental contact, reduces the risk of fire. Disadvantages: Can restrict access for maintenance, may trap heat.
- Isolation:Separating electrical circuits or equipment to prevent faults from spreading. Advantages: Limits the extent of damage, improves safety. Disadvantages: Can be complex and costly to implement.
Application Considerations

Selecting the appropriate protection method from Table 8.3.1 requires careful consideration of several factors. These include:
Electrical Equipment Type
- The type of electrical equipment (e.g., motors, generators, transformers) will influence the potential hazards and the suitability of different protection methods.
Environmental Conditions
- The environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, presence of flammable gases) can affect the effectiveness and safety of certain protection methods.
Maintenance Requirements
- The frequency and complexity of maintenance procedures associated with different protection methods should be considered to ensure cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Cost Considerations
- The initial cost and ongoing maintenance expenses of different protection methods must be evaluated to determine the most cost-effective solution.
Example Application
For instance, in an industrial setting with high levels of flammable gases, an explosion-proof enclosure (Method E) would be an appropriate choice for protecting electrical equipment. Conversely, in a data center with controlled environmental conditions, a dry chemical fire suppression system (Method C) may be a suitable option.
Code Compliance
Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 is a crucial tool for ensuring compliance with the electrical code. It provides detailed guidance on the types of electrical equipment, protection methods, and application considerations for various electrical installations.
Table 8.3.1 in NFPA 10 is a helpful resource for understanding electrical requirements. While it may not contain the specific numbers you’re looking for, like the numeros del 100 al 500 , it does provide valuable information on electrical safety and compliance.
Consulting Table 8.3.1 can help ensure your electrical installations meet the necessary standards.
Using the table correctly is essential to avoid electrical hazards. By following the recommendations Artikeld in the table, electrical professionals can ensure that electrical systems are designed, installed, and maintained in accordance with the code, minimizing the risk of electrical fires, shocks, and other accidents.
Code Enforcement
Electrical inspectors rely on Table 8.3.1 to verify compliance with the electrical code during inspections. By adhering to the table’s requirements, electrical contractors can demonstrate that their work meets the code’s standards, ensuring the safety of electrical installations.
Liability Mitigation
Proper use of Table 8.3.1 can help electrical contractors mitigate their liability in the event of an electrical accident. By following the code’s requirements, contractors can demonstrate that they exercised due diligence in designing and installing electrical systems, reducing their legal exposure.
Design Considerations
Table 8.3.1 is a valuable resource for electrical engineers and designers. It provides guidance on the selection of appropriate protection methods for various types of electrical equipment. By understanding the information in the table, designers can optimize protection and minimize electrical risks.
Selecting Protection Methods
To select the appropriate protection method for a particular piece of equipment, designers should consider the following factors:
- Type of equipment
- Electrical characteristics of the equipment
- Environmental conditions
- Code requirements
By considering these factors, designers can select the protection method that best meets the specific needs of the application.
Optimizing Protection
Table 8.3.1 can also be used to optimize protection. By selecting the protection method that is best suited for the equipment and application, designers can reduce the risk of electrical fires and other hazards. The table can also help designers to identify potential problems and to develop mitigation strategies.
Essential FAQs: Table 8.3.1 In Nfpa 10
What types of electrical equipment are covered in Table 8.3.1?
Table 8.3.1 encompasses a wide range of electrical equipment, including transformers, generators, motors, and switchgear.
How can I select the appropriate protection method for my electrical equipment?
Table 8.3.1 provides guidance on selecting protection methods based on factors such as equipment type, operating conditions, and potential hazards.
What are the advantages of using Table 8.3.1?
Table 8.3.1 ensures code compliance, optimizes protection strategies, minimizes electrical risks, and enhances system reliability.