Cones and polyhedrons both have only one base – Cones and polyhedrons, two distinct geometric shapes, share a striking commonality: they both possess only one base. This shared feature has a profound impact on their geometry, applications, and overall characteristics, making them intriguing subjects for exploration.
Delving into the world of cones and polyhedrons, we will uncover the intricacies of their definitions, delve into their shared properties, and unravel the unique differences that set them apart. Furthermore, we will investigate the practical applications of these shapes, showcasing their versatility and significance in various fields.
Definitions: Cones And Polyhedrons Both Have Only One Base
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure with a circular base and a single vertex. The vertex is connected to all points on the circumference of the base by line segments, forming a cone-shaped surface.
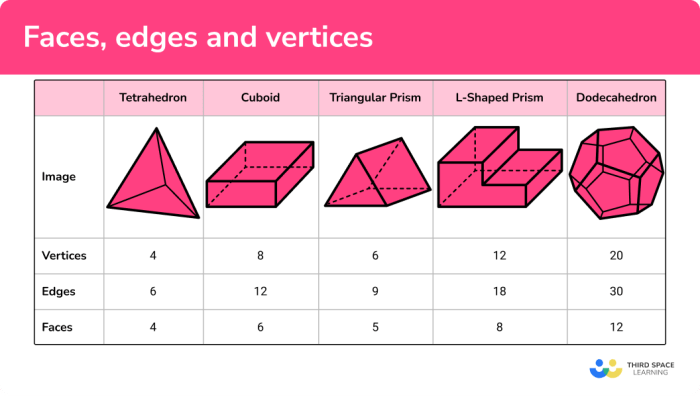
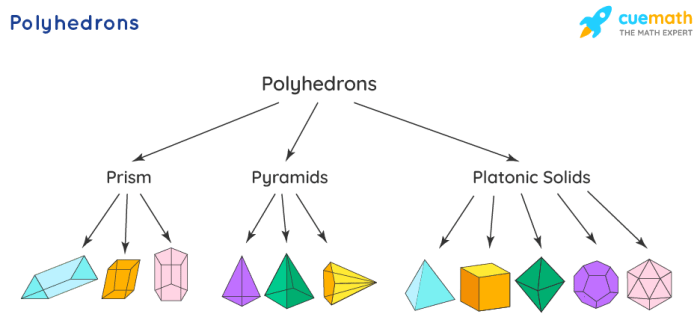
A polyhedron is a three-dimensional figure composed of flat, polygonal faces that are connected by edges. Polyhedra have a finite number of faces, edges, and vertices.
The base of a cone or polyhedron is the polygon that forms the bottom surface of the shape.
Commonalities
Both cones and polyhedrons can have only one base. This shared feature means that the base of the shape is the only polygon that is not part of the cone’s or polyhedron’s surface.
Examples of cones and polyhedrons with one base include:
- Cones: A right circular cone, an oblique circular cone
- Polyhedrons: A square pyramid, a triangular prism
The presence of a single base impacts the geometry of these shapes by defining the shape’s overall form and determining the number of faces, edges, and vertices.
Differences
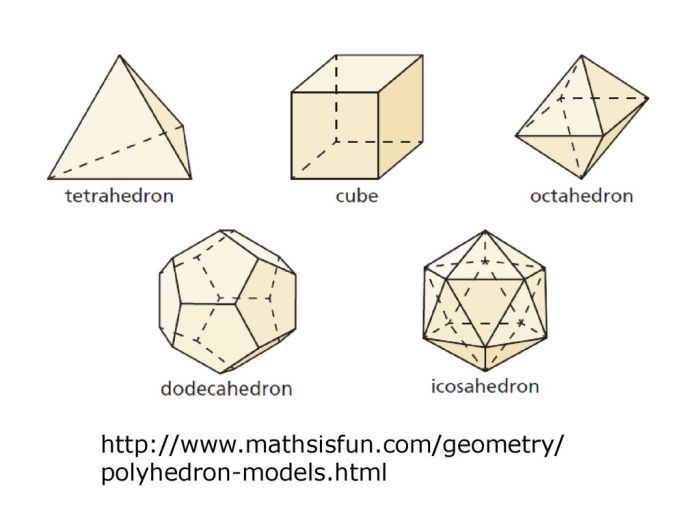
The key difference between cones and polyhedrons is that cones have curved surfaces while polyhedrons have flat surfaces. Additionally, cones have only one base, while polyhedrons can have multiple bases.
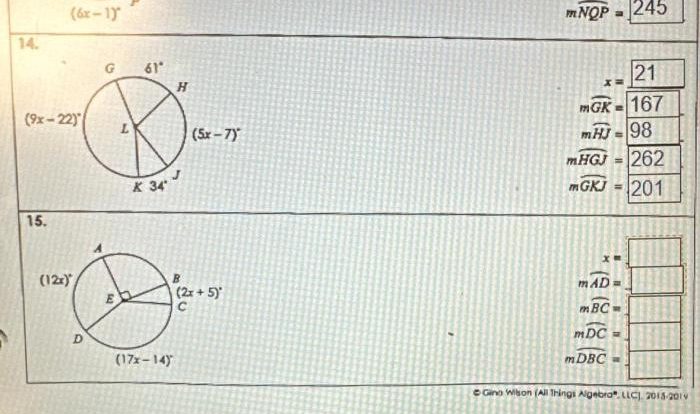
The number of faces, edges, and vertices also varies between cones and polyhedrons. Cones have one base, one curved surface, and one vertex, while polyhedrons have multiple faces, multiple edges, and multiple vertices.
The distinct properties that distinguish cones from polyhedrons include the shape of their surfaces, the number of their bases, and the number of their faces, edges, and vertices.
Applications
Cones and polyhedrons with one base are used in a variety of real-world applications, including:
- Cones: Traffic cones, ice cream cones, party hats
- Polyhedrons: Pyramids (architecture), prisms (prisms used in optics)
The unique properties of these shapes contribute to their functionality. For example, the cone’s curved surface allows it to roll smoothly, making it ideal for use as a traffic cone. The polyhedron’s flat surfaces allow it to be easily stacked, making it useful for building structures like pyramids.
The advantages of using cones and polyhedrons with one base include their structural stability, their ability to be easily manufactured, and their wide range of applications.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the main difference between a cone and a polyhedron?
Cones are curved surfaces with a circular base, while polyhedrons are three-dimensional shapes with flat faces and straight edges.
How does the number of faces and edges vary between cones and polyhedrons?
Cones have one base and one curved surface, while polyhedrons have multiple faces and edges.
What are some real-world applications of cones and polyhedrons?
Cones are used in traffic cones, ice cream cones, and loudspeakers. Polyhedrons are used in dice, crystals, and architectural structures.