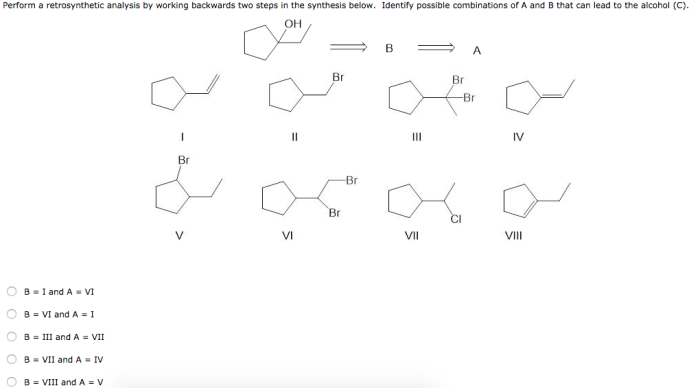
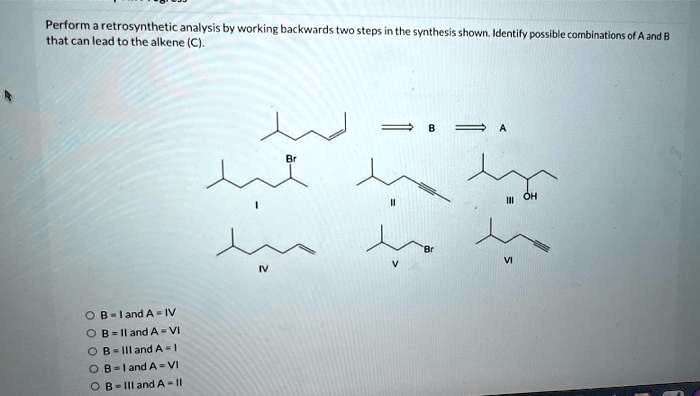
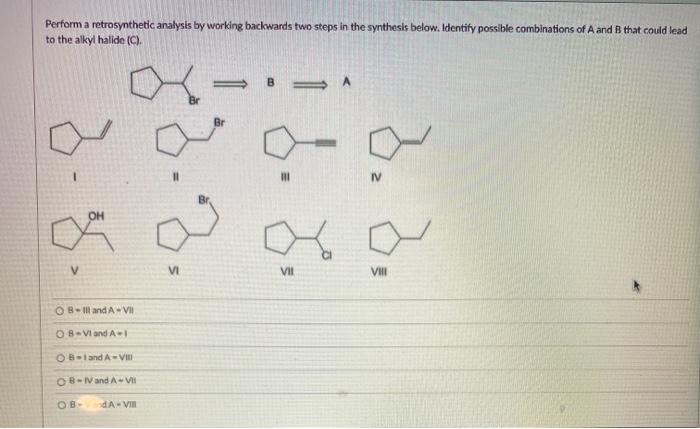
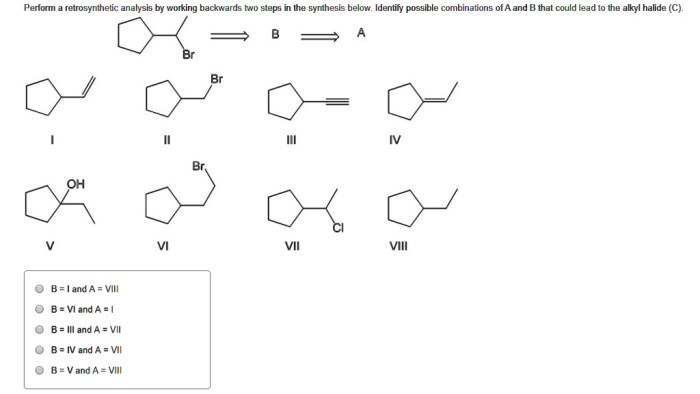
Perform a retrosynthetic analysis by working backwards – Retrosynthetic analysis, a fundamental technique in organic chemistry, empowers chemists to unravel the intricate architecture of molecules by working backwards from a target compound. This systematic approach guides the dissection of complex molecules into simpler building blocks, revealing the synthetic pathways that lead to their construction.
By embarking on a retrosynthetic journey, chemists gain invaluable insights into the molecular architecture, enabling them to devise efficient and targeted synthetic strategies.
Introduction
Retrosynthetic analysis is a powerful tool in organic chemistry that enables chemists to design synthetic pathways for target molecules. It involves working backwards from the target molecule to identify the simpler building blocks and reagents required for its synthesis.
Working Backwards
The key to retrosynthetic analysis is to work backwards. This involves breaking down the target molecule into smaller and simpler fragments, identifying the functional groups present, and determining the possible synthetic routes to obtain these fragments.
Identifying Functional Groups, Perform a retrosynthetic analysis by working backwards
Functional groups play a crucial role in retrosynthetic analysis. They determine the reactivity and properties of the molecule and provide clues to the synthetic pathways that can be employed.
Identifying functional groups involves analyzing the structure of the target molecule and recognizing the characteristic patterns of atoms and bonds that define each functional group.
Retrosynthesis Strategies
There are several common retrosynthesis strategies that can be employed:
- Functional group interconversion:This strategy involves converting one functional group into another through a series of reactions.
- Disconnection reactions:This strategy involves breaking down the target molecule into smaller fragments by cleaving specific bonds.
- Retro Diels-Alder reaction:This strategy is used to synthesize cyclic compounds by reversing the Diels-Alder reaction.
Examples and Applications: Perform A Retrosynthetic Analysis By Working Backwards
Retrosynthetic analysis is widely used in drug design, natural product synthesis, and other areas of organic chemistry.
For example, in drug design, retrosynthetic analysis can be used to identify potential lead compounds and design synthetic pathways for their synthesis.
Detailed FAQs
What is the essence of retrosynthetic analysis?
Retrosynthetic analysis is a technique that allows chemists to design synthetic pathways for target molecules by working backwards from the desired product, breaking it down into simpler building blocks and identifying potential synthetic routes.
Why is working backwards crucial in retrosynthesis?
Working backwards enables chemists to identify the functional groups and structural features that are necessary for the target molecule, guiding them towards efficient and selective synthetic strategies.
How do functional groups play a role in retrosynthesis?
Functional groups serve as the key recognition points in retrosynthesis. By identifying and analyzing functional groups within a target molecule, chemists can deduce the potential synthetic routes and the building blocks required for its construction.