Embark on an enlightening journey with the Unit 10 Circles Homework 3 Answer Key, your ultimate guide to mastering the intricacies of circles. Delve into the fundamental concepts, unravel the mysteries of equations, and explore the captivating world of inscribed and circumscribed figures, tangent lines, and sectors.
Unveiling the secrets of circles, this comprehensive guide provides step-by-step solutions to complex equations, empowering you to conquer any circle-related challenge with confidence. Prepare to witness the seamless integration of theory and practice as we navigate the fascinating realm of geometry.
Circles: Fundamental Concepts and Properties: Unit 10 Circles Homework 3 Answer Key
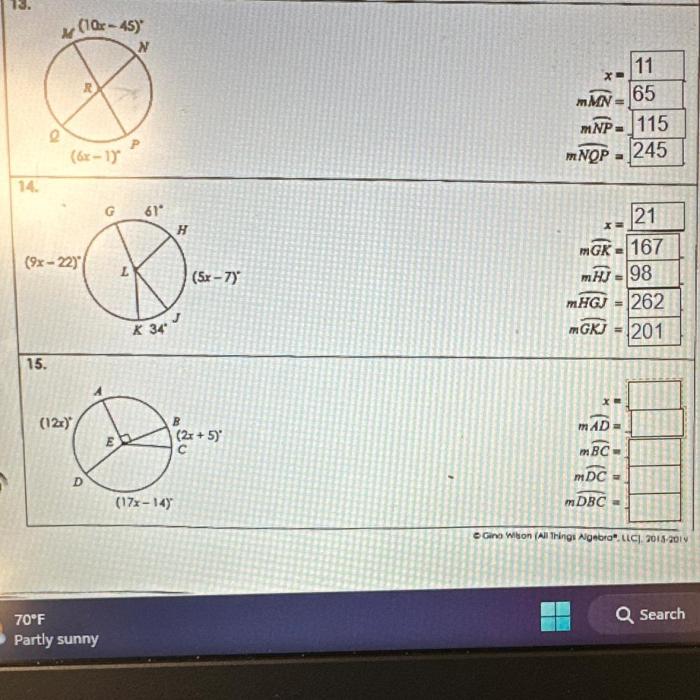
Circles are closed, two-dimensional figures defined by a constant distance from a fixed point, known as the center. They exhibit unique properties and are fundamental in various mathematical applications.
Key Concepts
- Radius:The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Diameter:The distance across the circle through the center, equal to twice the radius.
- Circumference:The distance around the circle, calculated using the formula 2πr, where r is the radius.
- Symmetry:Circles possess radial symmetry, meaning they can be rotated around their center to appear identical at any angle.
- Congruence:Two circles are congruent if they have the same radius and, therefore, the same circumference.
Solving Equations
Equations involving circles can be solved using algebraic techniques. Here are the steps:
- Identify the variable to be solved for.
- Use the relevant formula, such as the circumference formula (2πr) or the area formula (πr²).
- Substitute known values and simplify the equation.
- Solve for the variable using algebraic operations.
For example, to find the radius of a circle with a circumference of 20π, use the formula 2πr = 20π and solve for r: 2πr = 20π, r = 10.
Area and Circumference
The area and circumference of circles are calculated using specific formulas:
- Area:A = πr², where r is the radius.
- Circumference:C = 2πr, where r is the radius.
The radius is a key factor in determining these measurements. A larger radius results in a larger area and circumference.
Inscribed and Circumscribed Figures
Inscribed and circumscribed figures are shapes that interact with circles in specific ways:
- Inscribed Figure:A figure that lies entirely within a circle, with all its vertices touching the circle.
- Circumscribed Figure:A figure that encloses a circle, with all its sides tangent to the circle.
To find the radius of an inscribed circle, use the formula r = s/2n, where s is the perimeter of the inscribed polygon and n is the number of sides. For a circumscribed circle, use the formula r = a/2, where a is the side length of the circumscribed square.
Tangent Lines, Unit 10 circles homework 3 answer key
Tangent lines are lines that touch a circle at exactly one point:
- Tangent Line Property:A tangent line is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency.
- Tangent Line Equation:The equation of a tangent line to a circle centered at (h, k) with radius r is (x – h)² + (y – k)² = r².
Sector and Segment
Sectors and segments are parts of circles defined by arcs and chords:
- Sector:A region of a circle bounded by two radii and the intercepted arc.
- Segment:A region of a circle bounded by a chord and the intercepted arc.
The area of a sector is calculated using the formula A = (θ/360°)πr², where θ is the central angle in degrees and r is the radius. The arc length of a sector is calculated using the formula s = (θ/360°)2πr, where θ is the central angle in degrees and r is the radius.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the formula for the circumference of a circle?
C = 2πr
How do I find the area of a circle?
A = πr²
What is the relationship between the radius and diameter of a circle?
Diameter = 2 × Radius